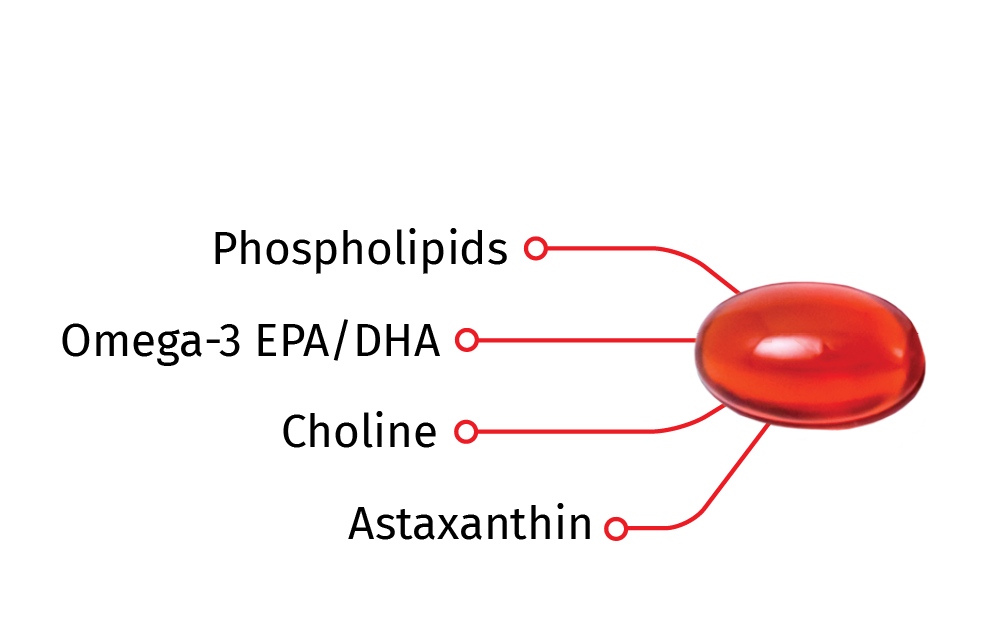
The Power of Krill Oil
What sets krill oil apart from other omega-3 EPA/DHA sources is its powerhouse combination of nutrients and superior bio-availability. Packed with omega-3s bound to phospholipids, choline, and the potent antioxidant astaxanthin, krill oil delivers more than just omega-3s—it's a complete nutrient package. This unique structure allows for better cellular uptake and utilization by the body, giving it a clear advantage over traditional omega-3 sources.
6 Key Advantages of Krill Oil

Pure and Sustainable
Krill oil is one of the purest and most sustainable sources of omega-3 EPA/DHA. It's naturally pristine environment, the abundance and reproductive ability of krill along with the active and regulated sustainability practices all contribute to the purity and sustainability of krill oil.
PRISTINE ENVIRONMENT
Krill are harvested from the Southern Ocean, one of the least contaminated envrionments on Earth. This ensures that krill are less likely to accumulate contaminants like heavy metals, dioxins, and microplastics compared to fish species from more polluted waters.
LOW IN FOOD CHAIN
Krill's place at the bottom of the marine food chain reduces the likelihood of bioaccumulation of toxins that are often found in species higher up the food chain.
LESS THAN 1% FISHED
To help protect and maintain the krill biomass, its fishing is regulated by the Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Life Resources (CCAMLR). The krill fishery is tightly regulated, with quotas limiting the catch to less than 1% of the krill biomass, helping preserve the marine ecosystem.
500 MILLION METRIC TONS
That is the amount of krill in the ocean which is 2X the human biomass. A female krill can produce between 6,000 and 10,000 eggs in a single spawning event. Krill can spawn multiple times during a breeding season, potentially laying hundreds of thousands of eggs over their lifespan.

PHOSPHOLIPIDS
Krill oil contains omega-3 EPA/DHA bound to phospholipids, unlike the triglycerides found in fish oil. Phospholipids are a vital component of cell membranes and are involved in various cellular functions, including signaling, cell structure, and nutrient transport.1 They make omega-3s more bioavailable and easily absorbed into the body’s cells
Learn more

OMEGA-3 EPA/DHA
Krill oil supplies omega-3 EPA/DHA, which is an important nutrient that 4 in 5 people don’t get enough of in their diet2. It helps support many aspects of health including heart, brain, joint, immunity, women’s health, and sports performance.
Learn more

CHOLINE
Krill oil contains choline, which is an essential nutrient that 9 in 10 people don’t get enough of in their diet.3 It plays several critical roles in the body, particularly in maintaining the structural integrity of cell membranes, facilitating nerve signaling, and supporting metabolic processes. It supports the body by maintaining brain, liver, heart, and muscle health.
Learn more

ASTAXANTHIN
The astaxanthin that natural occurs in krill oil gives that red coloring and helps protect the omega-3 EPA/DHA from oxidation, allowing the oil to remain stable without the need for additional preservatives. It is renowned for its powerful antioxidant properties, which are considered up to 6,000 times stronger than Vitamin C4 playing a vital role in protecting cells from oxidative stress.
Learn more
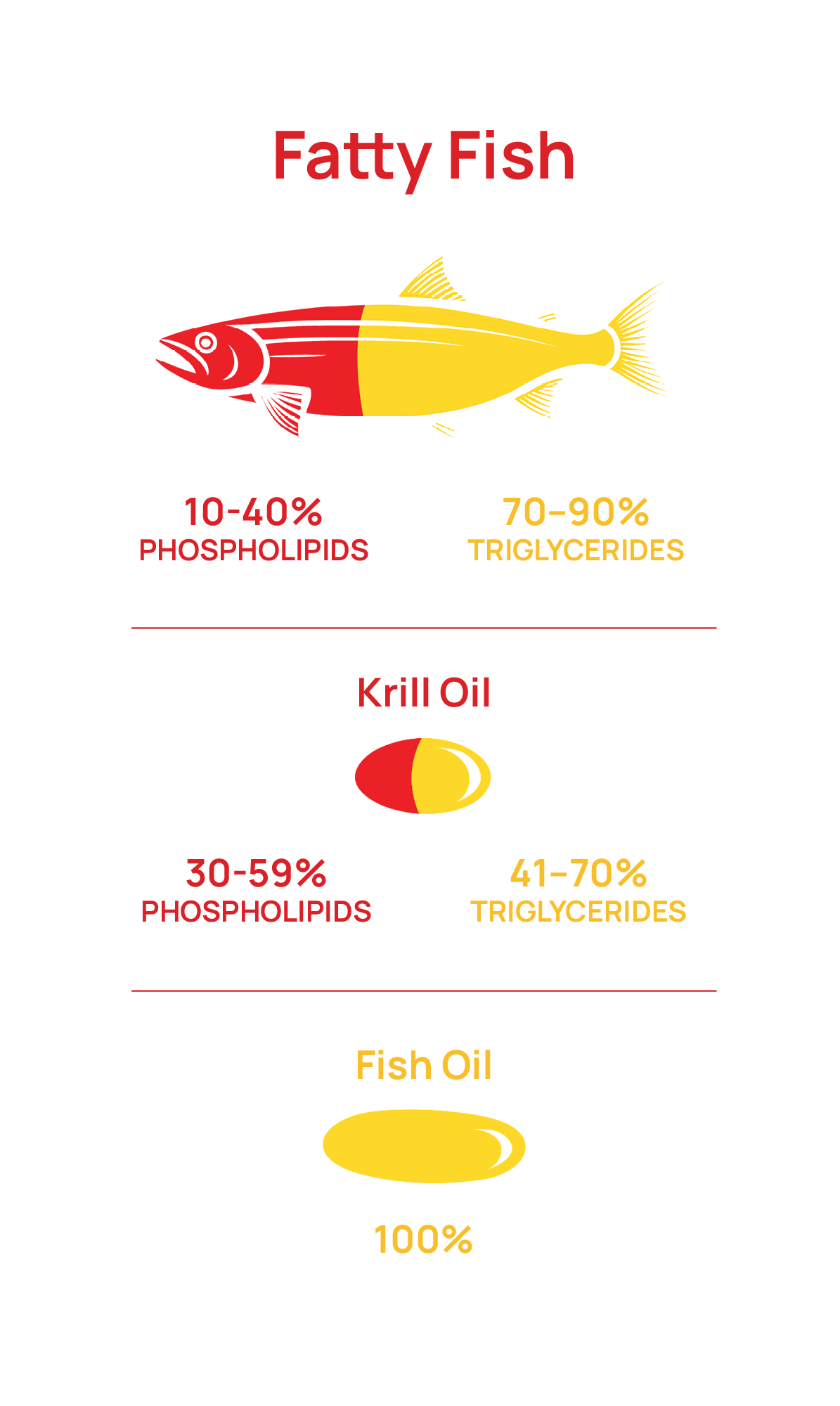
FAT COMPOSITION
Krill oil is more like fatty fish vs fish oil
Fatty fish such as herring, mackerel and salmon are made up of phospholipid and triglyceride omega-3 EPA/DHA.5,6 Krill oil is also made up of phospholipids and triglycerides while fish oils are 100% made of triglycerides. This makes krill oil closer to eating real fatty fish.
Fish oil lacks phospholipids primarily because the omega-3s are sourced from muscle tissue, where triglycerides dominate as the form of fat storage, rather than phospholipids which are found in cell membranes. In contrast, krill oil has a high concentration of phospholipids because krill store a significant portion of their omega-3s in their cell membranes.
High quality krill oil is made up of 40%+ phospholipids.
See how krill oil compostion compares to eating the following fatty fish:
|
Fish Type |
Phospholipids |
Triglycerides |
| Herring | 20-30% | 70-80% |
| Mackerel | 15-25% | 75-85% |
| Sardines | 15-20% | 80-85% |
| Anchovies | 10-15% | 85-90% |
NO FISHY BURPS OR AFTERTASTE
Easily Digestible
In krill oil, the omega-3 EPA/DHA are bound to phospholipids, whereas in fish oil, they are primarily bound to triglycerides. Krill oil’s phospholipids act as natural emulsifiers, which help fat-soluble nutrients like omega-3s mix with the water-based digestive fluids. This makes krill oil easier to digest and absorb compared to fish oil, which relies on bile for emulsification.
- Micelle Formation: Phospholipids form micelles in the digestive tract, which are small particles that encapsulate fat-soluble nutrients, including omega-3s. This process enhances the solubility of these fats in the water-based environment of the intestines, making it easier for the body to absorb them.
In fish oil, omega-3s are bound to triglycerides which are fats that float to the top of the stomach and can cause fishy burps. The body has to work harder and use additional processes to break down and digest fish oil. A fatty meal is usually recommended to help with its digestion.
BACKED BY 7 HUMAN CLINICAL TRIALS
More Bioavailable
One of the most important reasons for krill oil's superior bioavailability is that its omega-3 EPA/DHA are primarily bound to phospholipids, unlike fish oil, where they are bound to triglycerides. This difference significantly impacts how the body absorbs and utilizes these essential fatty acids.
Here's why:
- Phospholipids Make up our Cell Membranes: Phospholipids are a natural component of cell membranes. Because of this, the body readily recognizes and integrates them. This allows the omega-3s in krill oil to be absorbed more efficiently at the cellular level.
- Direct Absorption into Cells: Phospholipid-bound omega-3s can be more easily incorporated into cell membranes. This means that less omega-3s are used as energy, and more is directly available to tissues and organs like the heart, liver, and brain.
Backed by over 135 total studies including 50+ human clinical studies, krill oil supports heart, joint, brain, liver, eye, women's, skin, muscle, athletic and general overall health.










Before adding any dietary supplement to your routine, including krill oil, we recommend talking with your healthcare provider – especially if you have any pre-existing health conditions, take medication, or are pregnant/nursing. Dietary supplements are not meant to substitute a healthy diet and exercise. Note: Krill oil contains crustacean shellfish.
References:
- Alberts, B., Johnson, A., Lewis, J., Raff, M., Roberts, K., & Walter, P. (2015). Molecular biology of the cell (6th ed.). Garland Science.
- National Center for Health Statistics. (2018, November). Births in the United States, 2017 (Data Brief No. 321). Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db321.htm
- Chou, Y., Huang, W., Chen, M., Wang, Y., & Hsu, Y. (2016). Effective treatment with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation combined with hemoperfusion in two patients with carbamazepine intoxication. Medicine, 95(9), e2996. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000002996
- Fassett, R. G., & Coombes, J. S. (2011). Astaxanthin in cardiovascular health and disease. Molecules, 16(6), 4481-4494. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16064481
- Brossard, N., Croset, M., & Normand, S. (1996). Plasma cholesterol esterification and phospholipid-fatty acid profiles in humans after short-, middle-, and long-term fish oil intake. Lipids, 31(5), 487–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02522745
- USDA. (n.d.). Fish and fish products. USDA Food Composition Databases. Retrieved from https://fdc.nal.usda.gov